Managing Inconsistent, Duplicate, and Non-Equivalent Spare Parts in a Busy Factory
Managing Inconsistent, Duplicate, and Non-Equivalent Spare Parts in a Busy Factory
In a busy factory environment, managing spare parts inventory is complex. You deal with parts from multiple manufacturers and distributors, each with different naming conventions, leading to duplicate records, over-purchasing, and operational inefficiencies. This can result in significant amounts of capital tied up in excess stock, inaccurate procurement, and production delays.
As you embark on a new capital project, these challenges increase, making it harder to control inventory and potentially leading to over-purchasing of the same parts under different names.
KOIOS Solution: A Data-Driven Approach to Spare Parts Management
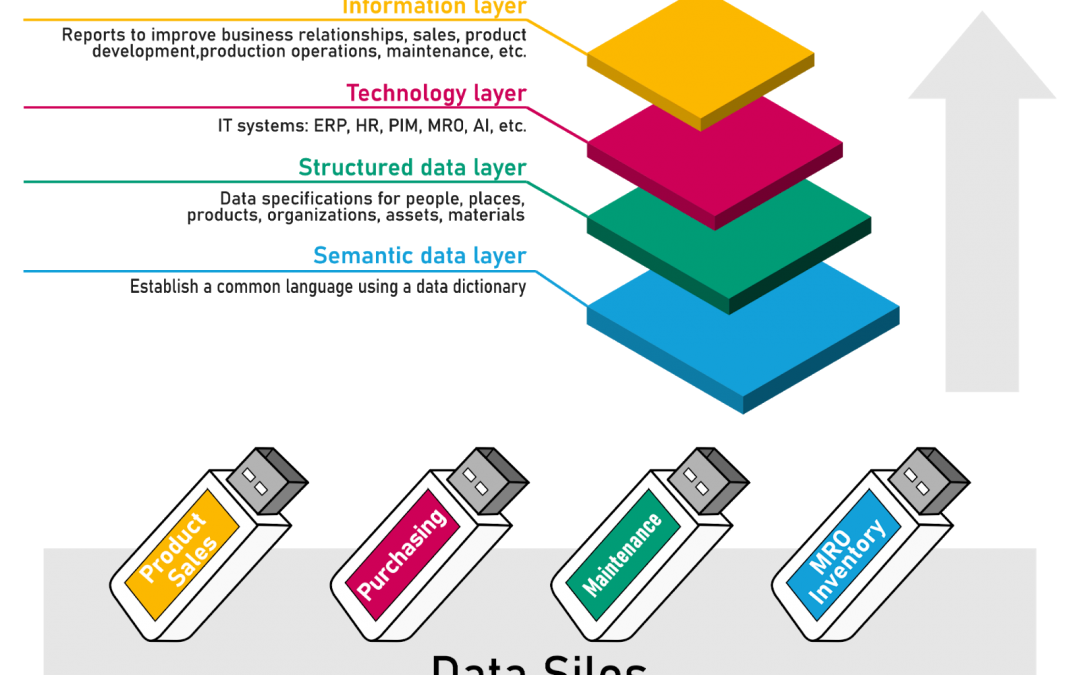
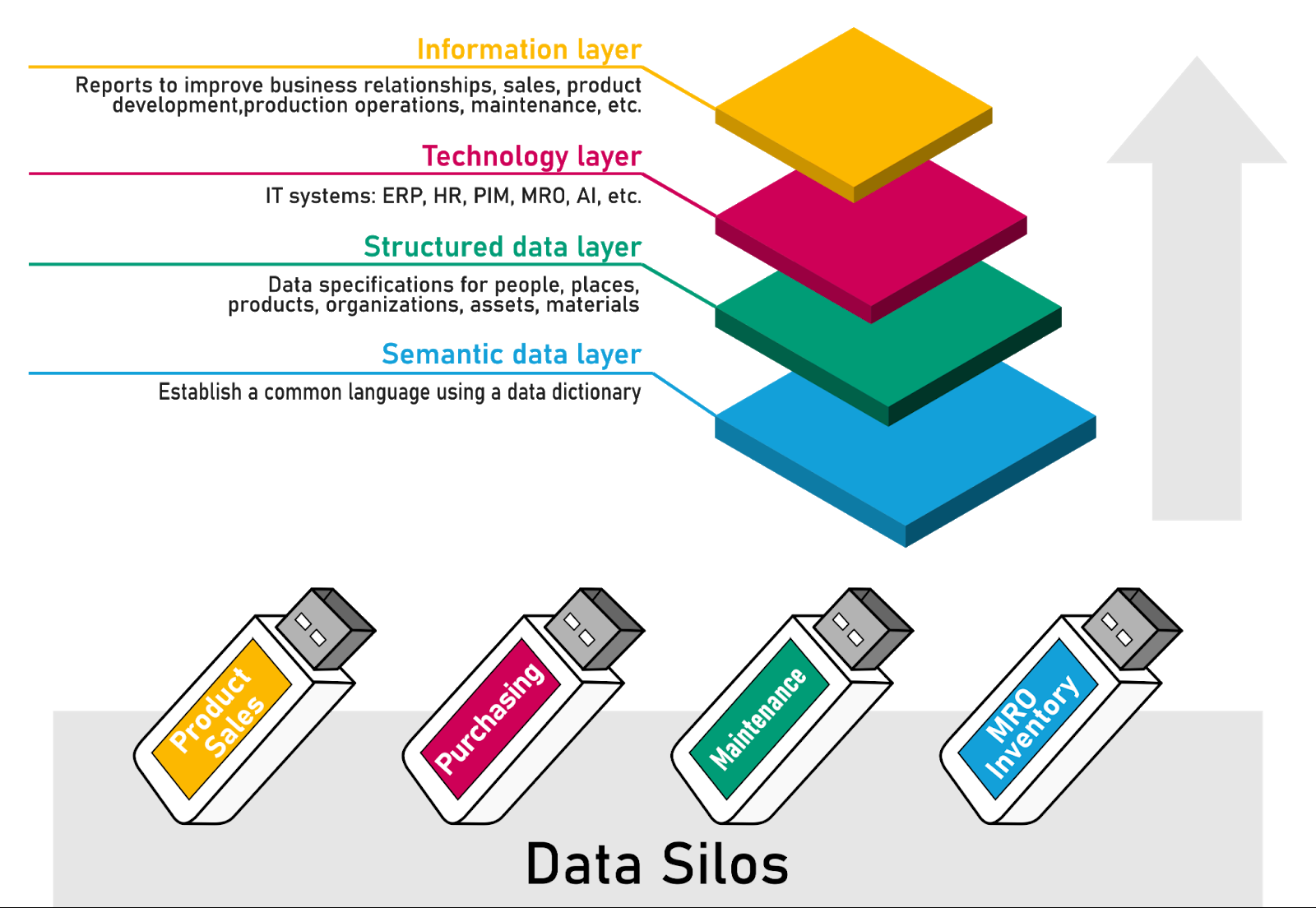
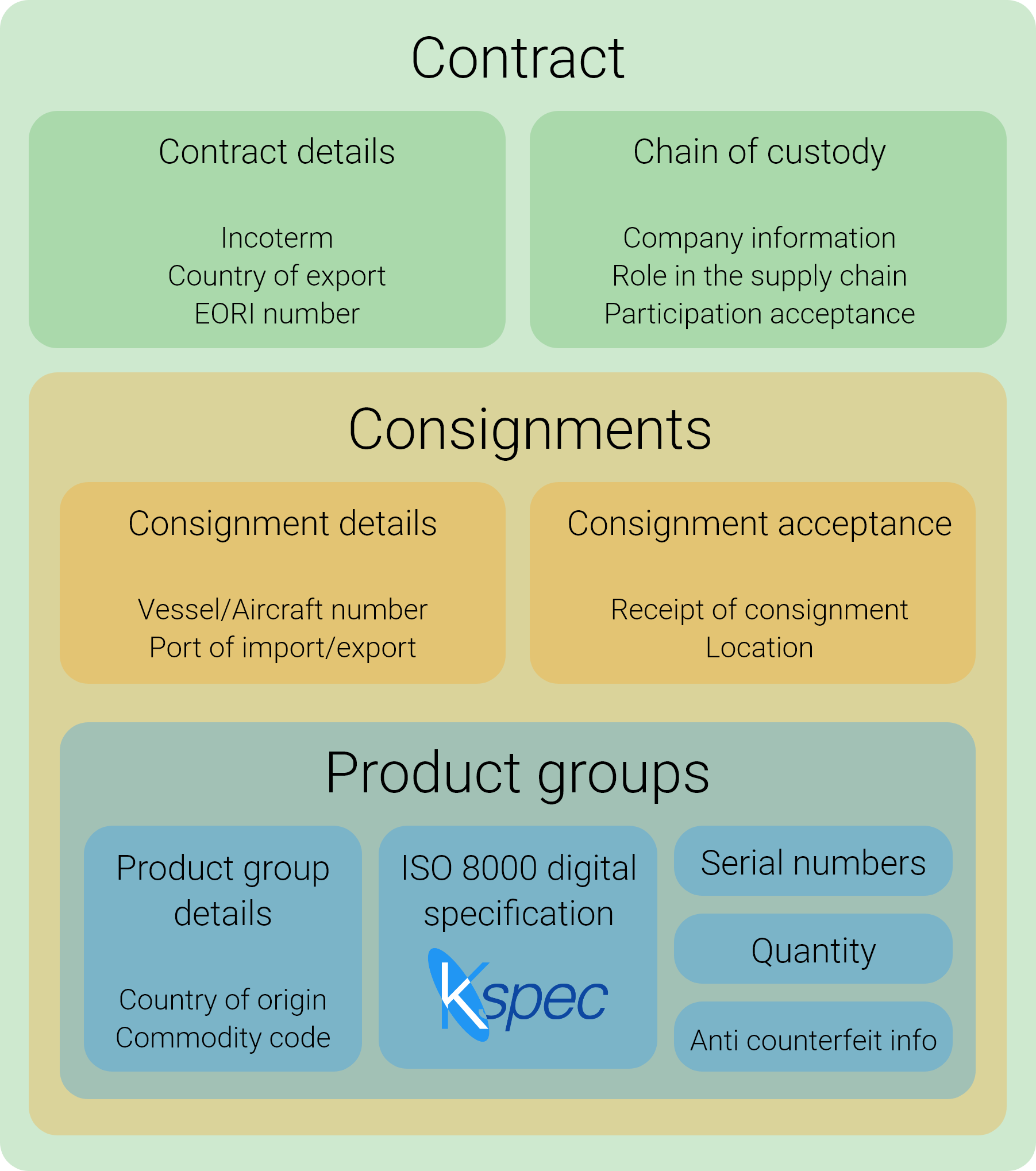
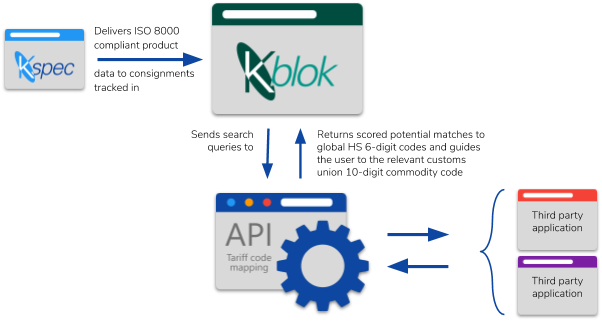
KOIOS offers a data cleansing and governance solution that standardizes spare parts data in your ERP system, reducing duplication, identifying equivalent parts, and optimizing your procurement process. By creating a single source of truth, KOIOS enables you to reduce working capital, improve operational efficiency, and make better decisions based on clean, real-time data.
Key Benefits of KOIOS for Spare Parts Management in a Factory Setting
1. Reduction in Working Capital
Minimized Overstock Through Equivalence Matching: By identifying duplicate and equivalent parts in your system, KOIOS reduces unnecessary stock. In a typical manufacturing setting, inventory levels can be reduced by 10% to 20%. For example, in a factory with $2 million worth of spare parts in stock, KOIOS could free up $200,000 to $400,000 in working capital.
Eliminate Redundant Purchases: In a busy factory, ordering duplicate parts is common due to different naming conventions across suppliers. KOIOS standardizes this data, reducing duplicate orders and freeing up an additional 5% to 10% of your procurement budget, potentially saving $50,000 to $100,000 annually in unnecessary purchases.
2. Operational Efficiencies in a Fast-Paced Environment
Accurate Material Bills of Materials (BoMs): KOIOS generates clean, standardized BoMs, ensuring that only necessary parts are ordered for projects. By reducing over-ordering and ensuring the right parts are available, KOIOS can reduce procurement lead times by 15% to 30%, which translates into faster project completions and fewer production delays.
Reduced Manual Effort: Automated data cleansing and the identification of equivalent parts can reduce the time spent on manual data management by 50%, allowing your procurement and warehouse teams to focus on higher-value activities.
Supplier Optimization: With clear equivalence data, KOIOS enables you to compare prices and lead times across suppliers more effectively, improving your negotiation position and reducing part costs by 5% to 15%.
3. Improved Data Quality and Governance
Single Source of Truth: KOIOS eliminates inconsistencies and duplicates, ensuring that both warehouse and procurement teams work from accurate, standardized information. Improved data quality can reduce ordering errors by 20%, leading to smoother operations and fewer unexpected shortages or delays.
Ongoing Data Governance: KOIOS provides continuous monitoring and updates to your data, ensuring that new parts introduced during your capital project are standardized from the outset, preventing future duplications and improving long-term inventory management.
4. Cost Savings in a Factory Context
Procurement Savings from Equivalence Substitution: KOIOS’ ability to identify equivalent parts across suppliers allows you to choose the most cost-effective option. This flexibility can reduce procurement costs by 5% to 10%, potentially saving $50,000 to $100,000 annually, depending on the scale of your operation.
Optimized Warehouse Space: By reducing redundant and overstocked inventory, KOIOS helps you optimize your warehouse space, potentially reducing storage costs by 10% to 15%. In a factory where warehouse costs total $200,000 annually, this can mean a $20,000 to $30,000 reduction.
5. Decision-Making Control and Flexibility
Empowered Teams with Real-Time Data: KOIOS provides real-time, accurate data to both warehouse and procurement teams, giving them the insights they need to make informed decisions. With clean data and equivalence matching, they can act quickly to substitute parts or negotiate with suppliers, reducing downtime by up to 20%.
Future-Proof for Capital Projects: As new parts are introduced during your capital project, KOIOS ensures that they are seamlessly integrated into your ERP system, preventing future issues of mismanagement and duplication. This reduces the administrative burden by 30%, freeing up time for more strategic activities.
Equivalence: A Game Changer in Spare Parts Management
In the real-world operations of a busy factory, recognizing equivalent parts is crucial for reducing unnecessary purchases and ensuring operational efficiency. KOIOS identifies interchangeable parts, allowing you to make faster, more informed decisions when sourcing from different suppliers. This reduces your reliance on single suppliers and improves your flexibility in managing unexpected shortages or price fluctuations.
Conclusion: Significant Financial and Operational Gains with KOIOS
KOIOS is a powerful solution for the real-world challenges of managing spare parts in a factory environment. By cleansing and standardizing your ERP data, identifying equivalences, and improving governance, KOIOS can reduce your working capital requirements, improve procurement efficiency, and save significant costs. For a factory with a $2 million spare parts inventory, KOIOS could deliver savings of $300,000 to $500,000 through reduced inventory levels, better procurement choices, and optimized warehouse space.
With KOIOS, you gain control over your spare parts data, allowing your teams to make smarter, faster decisions, and ensuring that your operations run smoothly — both during day-to-day activities and new capital projects.